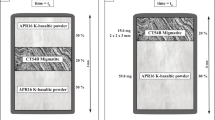
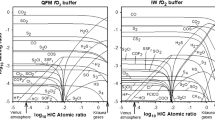
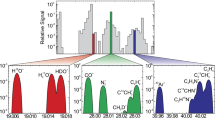
Abstract
New observations from the Venus Express spacecraft as well as theoretical and experimental investigation of Venus analogue materials have advanced our understanding of the petrology of Venus melts and the mineralogy of rocks on the surface. The VIRTIS instrument aboard Venus Express provided a map of the southern hemisphere of Venus at ∼1 μm allowing, for the first time, the definition of surface units in terms of their 1 μm emissivity and derived mineralogy. Tessera terrain has lower emissivity than the presumably basaltic plains, consistent with a more silica-rich or felsic mineralogy. Thermodynamic modeling and experimental production of melts with Venera and Vega starting compositions predict derivative melts that range from mafic to felsic. Large volumes of felsic melts require water and may link the formation of tesserae to the presence of a Venus ocean. Low emissivity rocks may also be produced by atmosphere-surface weathering reactions unlike those seen presently.
High 1 μm emissivity values correlate to stratigraphically recent flows and have been used with theoretical and experimental predictions of basalt weathering to identify regions of recent volcanism. The timescale of this volcanism is currently constrained by the weathering of magnetite (higher emissivity) in fresh basalts to hematite (lower emissivity) in Venus’ oxidizing environment. Recent volcanism is corroborated by transient thermal anomalies identified by the VMC instrument aboard Venus Express. The interpretation of all emissivity data depends critically on understanding the composition of surface materials, kinetics of rock weathering and their measurement under Venus conditions.
Extended theoretical studies, continued analysis of earlier spacecraft results, new atmospheric data, and measurements of mineral stability under Venus conditions have improved our understanding atmosphere-surface interactions. The calcite-wollastonite CO2 buffer has been discounted due, among other things, to the rarity of wollastonite and instability of carbonate at the Venus surface. Sulfur in the Venus atmosphere has been shown experimentally to react with Ca in surface minerals to produce anhydrite. The extent of this SO2 buffer is constrained by the Ca content of surface rocks and sulfur content of the atmosphere, both of which are likely variable, perhaps due to active volcanism. Experimental work on a range of semiconductor and ferroelectric minerals is placing constraints on the cause(s) of Venus’ anomalously radar bright highlands.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Adamchik, A.L. Draper, The temperature dependence of the Urey equilibrium and the problem of CO2 content of the atmosphere of Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 11, 1303–1307 (1963)
J.B. Adams, A.L. Filice, Spectral reflectance 0.4 to 2.0 microns of silicate rock powders. J. Geophys. Res. 72(22), 5705–5715 (1967). doi:10.1029/JZ072i022p05705
D.A. Allen, J.W. Crawford, Cloud structure on the dark side of Venus. Nature 307, 222–224 (1984)
F.S. Anderson, S.E. Smrekar, Global mapping of crustal and lithospheric thickness on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 111, E08006 (2006). doi:10.1029/2004JE002395
J. Arkani-Hamed, On the tectonics of Venus. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 76, 75–96 (1993)
R.E. Arvidson, R.A. Brackett, M.K. Shepard, N.R. Izenberg, B. Fegley Jr., J.J. Plaut, Microwave signatures and surface properties of Ovda Regio and surroundings, Venus. Icarus 112, 171–186 (1994)
D.C. Aveline, W.J. Abbey, M. Choukroun, A.H. Treiman, M.D. Dyar, S.E. Smrekar, S.M. Feldman, Rock and mineral weathering experiments under model Venus conditions. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 42, 2165 (2011)
D.C. Bain, P.F.S. Ritchie, D.R. Clark, D.M.L. Duthie, Geochemistry and mineralogy of weathered basalt from Morvern. Scotland. Mineral. Mag. 43, 865–872 (1980)
K.H. Baines et al., Detection of sub-micron radiation from the surface of Venus by Cassini/VIMS. Icarus 48, 307–311 (2000)
V.L. Barsukov, V.P. Volkov, I.L. Khodakovsky, The crust of Venus: theoretical models of chemical and mineral composition. Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 13, A3–A9 (1982), J. Geophys. Res. 87
A.T. Basilevsky, E.V. Shalygin, D.V. Titov, W.J. Markiewicz, F. Scholten, Th. Roatsch, M.A. Kreslavsky, L.V. Moroz, N.I. Ignatiev, B. Fiethe, B. Osterloh, H. Michalik, Geologic interpretation of the near-infrared images of the surface taken by the Venus Monitoring Camera, Venus Express. Icarus 217, 434–450 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2011.11.003
M. Bauer, W.E. Klee, The monoclinic-hexagonal phase transition in chlorapatite. Eur. J. Mineral. 5, 307–316 (1993)
E.E. Bjonnes, V.L. Hansen, B. James, J.B. Swenson, Equilibrium resurfacing of Venus: results from new Monte Carlo modeling and implications for Venus surface histories. Icarus 217, 451–461 (2012)
B. Bonin, Extra-terrestrial igneous granites and related rocks: a review of their occurrence and petrogenesis. Lithos 153, 3–24 (2012)
R.A. Brackett, B. Fegley, R.E. Arvidson, Volatile transport on Venus and implications for surface geochemistry and geology. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 100, 1553–1563 (1995)
M. Brown, Granite: from genesis to emplacement. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 125, 1079–1113 (2013). doi:10.1130/B30877.1
E.A. Bruckenthal, R.B. Singer, Spectral effects of dehydration on phyllosilicates. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 18, 135 (1987)
M.A. Bullock, D.H. Grinspoon, The stability of climate on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 7521–7529 (1996)
M.A. Bullock, D.H. Grinspoon, The recent evolution of climate on Venus. Icarus 150, 19–37 (2001)
D.J.M. Burkhardt, T. Scherer, Surface oxidation of basalt glass/liquid. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 352, 241–247 (2006)
I.H. Campbell, S.R. Taylor, No water, no granites-no oceans, no continents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 10(11), 1061–1064 (1983)
B.A. Campbell, P.G. Rogers, B. Regio Venus, Integration of remote sensing data and terrestrial analogs for geologic analysis. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 99, 21153–21171 (1994)
B.A. Campbell, D.B. Campbell, C.H. DeVries, Surface processes in the Venus highlands: results from analysis of Magellan and Arecibo data. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 104, 1897–1916 (1999)
B.A. Campbell, D.B. Campbell, G.A. Morgan, L.M. Carter, M.C. Nolan, J.F. Chandler, Evidence for crater ejecta on Venus tessera terrain from Earth-based radar images. Icarus 250, 123–130 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2014.11.025
R.W. Carlson, K.H. Baines, Th. Encrenaz, F.W. Taylor, P. Drossart, L.W. Kamp, J.B. Pollack, E. Lellouch, A.D. Collard, S.B. Calcutt, D.H. Grinspoon, P.R. Weissman, W.D. Smythe, A.C. Ocampo, G.E. Danielson, F.P. Fanale, T.V. Johnson, H.H. Kieffer, D.L. Matson, T.B. McCord, L. Soderblom, Galileo infrared imaging spectroscopy measurements at Venus. Science 253, 1541–1548 (1991)
L.M. Carter, D.B. Campbell, B.A. Campbell, Volcanic deposits in shield fields and highland regions on Venus: surface properties from radar polarimetry. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 111, (E6) (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JE002519
A. Cathala, G. Berger, G.S. Pokrovski, Atmosphere-surface interactions at the Venus conditions: experiments and modeling. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 48, 1529 (2017)
E.A. Cloutis, F.C. Hawthorne, S.A. Mertzman, K. Krenn, M.A. Craig, D. Marcino, M. Methot, J. Strong, J.F. Mustard, D.L. Blaney, J.F. Bell III., F. Vilas, Detection and discrimination of sulfate minerals using reflectance spectroscopy. Icarus 184, 121–157 (2006)
G.B. Cook, R.F. Cooper, T. Wu, Chemical diffusion and crystalline nucleation during oxidation of ferrous iron-bearing magnesium aluminosilicate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 120, 207–222 (1990)
G.B. Cook, R.F. Cooper, Iron concentration and the physical processes of dynamic oxidation in an alkaline earth aluminosilicate glass. Am. Mineral. 85, 397–406 (2000)
R.F. Cooper, J.B. Fanselow, D.B. Poker, The mechanism of oxidation of a basaltic glass: chemical diffusion of network-modifying cations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 3253–3265 (1996)
D. Crisp, S. McNulldroch, S.K. Stephens, W.M. Sinton, B. Ragent, K.W. Ho- dapp, R.G. Probst, L.R. Doyle, D.A. Allen, J. Eias, Ground-based near-infrared imaging observations of Venus during the Galileo encounter. Science 253, 1538–1541 (1991)
J.A. Cutts, T.S. Balint, E. Chassefiere, E.A. Kolawa, Technology perspectives in the future exploration of Venus, in Exploring Venus as a Terrestrial Planet, ed. by L.W. Esposito, E.R. Stofan, T.E. Cravens. AGU Monograph Series, vol. 176 (2007), pp. 207–225, 250 pp.
A. Davaille, S.E. Smrekar, S. Tomlinson, Experimental and observational evidence for plume-induces subduction on Venus. Nat. Geosci. (2017). doi:10.1038/ngeo2928
C. de Bergh et al., Deuterium on Venus: observations from Earth. Science 251, 547–549 (1991)
P. D’Incecco, N. Müller, J. Helbert, M. D’Amore, Idunn Mons on Venus: location and extent of recently active lava flows. Planet. Space Sci. 136, 25–33 (2017)
T.M. Donahue, J.H. Hoffman, R.R. Hodges, A.J. Watson, Venus was wet: a measurement of the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen. Science 216, 630–633 (1982)
P. Drossart et al., Scientific goals for the observation of Venus by VIRTIS on ESA/Venus Express mission. Planet. Space Sci. 55, 1653–1672 (2007)
R.A. Eggleton, C. Foudoulis, D. Varkevisser, Weathering of basalt: changes in rock chemistry and mineralogy. Clays Clay Mineral. 35, 161–169 (1987)
L. Elkins-Tanton, S.E. Smrekar, P.C. Hess, E.M. Parmentier, Volcanism and volatile recycling on a one-plate planet: applications to Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 112, E04S06 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JE002793
R.E. Ernst, K.L. Buchan, D.W. Desnoyers, Plumes and plume clusters on Earth and Venus: evidence from large igneous provinces (LIPS), in Superplumes, ed. by D.A. Yuen et al.(Springer, Berlin, 2007), pp. 537–561
L.W. Esposito, Sulfur dioxide: episodic injection shows evidence for active Venus volcanism. Science 223, 1072–1074 (1984)
B. Fegley Jr., Venus. Treatise on Geochemistry, vol. 1 (2004, 2003), pp. 487–507
B. Fegley Jr., R.G. Prinn, Estimation of the rate of volcanism on Venus from reaction rate measurements. Nature 337(6202), 55–58 (1989)
B. Fegley Jr., A.H. Treiman, Chemistry of atmosphere-surface interactions on Venus and Mars, in Venus and Mars: Atmospheres, Ionospheres, and Solar Wind Interactions, ed. by J.G. Luhmann, M. Tatrallyay, R.O. Pepin (American Geophysical Union, Washington, 1992), pp. 7–71
B. Fegley Jr., A.H. Treiman, V.L. Sharpton, Venus surface mineralogy: observational and theoretical constraints, in Proceedings of Lunar and Planetary Science, vol. 22 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 1992), pp. 3–19
B. Fegley Jr., G. Klingelhöfer, R.A. Brackett, N. Izenberg, D.T. Kremser, K. Lodders, Basalt oxidation and the formation of hematite on the surface of Venus. Icarus 118, 373–383 (1995a)
B. Fegley Jr., K. Lodders, A.H. Treiman, G. Klingelhöfer, The rate of pyrite decomposition on the surface of Venus. Icarus 115, 159–180 (1995b)
B. Fegley Jr., G. Klingelhöfer, K. Lodders, T. Widemann, Geochemistry of surface-atmosphere interactions on Venus, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere, and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Philips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997a), pp. 591–636
B. Fegley Jr., M.Yu. Zolotov, K. Lodders, The oxidation state of the lower atmosphere and surface of Venus. Icarus 125, 416–439 (1997b)
J. Filiberto, Magmatic diversity on Venus: constraints from terrestrial analog crystallization experiments. Icarus 231, 131–136 (2014)
J. Filiberto, A.H. Treiman, Geochemistry of Venus basalts with constraints on magma genesis. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 48, 1148 (2017)
C.P. Florensky, O.V. Nikolaeva, V.P. Volkov, A.F. Kudryaskova, A.A. Pronin, Yu.M. Geektin, E.A. Tschaikina, A.S. Bashikirova, The oxidizing-reducing conditions on the surface of Venus according to the data of the “KONTRAST” geochemical indicator on the Venera 13 and Venera 14 spacecraft. Cosm. Res. 21, 278–281 (1983)
P.G. Ford, G.H. Pettengill, Venus: global surface radio emissivity. Science 220, 1379–1381 (1983)
P.G. Ford, G.H. Pettengill, Venus topography and kilometer-scale slopes. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 13,103–13,114 (1992)
I. Garate-Lopez, R. Jueso, A. Sánchez-Lavega, J. Peralta, G. Piccioni, P. Drossart, A chaotic long-lived vortex at the southern pole of Venus. Nat. Geosci. 6, 254–257 (2013)
J.B. Garvin, J.W. Head, G.H. Pettengill, S.H. Zisk, Venus global radar reflectivity and correlations with elevation. J. Geophy. Res. 90(B8), 6859–6871 (1985)
P. Gavin, V. Chevrier, Thermal alteration of nontronite and montorillonite: implications for the martian surface. Icarus 208, 721–734 (2010)
M.S. Gilmore, Tellus Regio, Venus: evidence of tectonic assembly of tessera terrain and implications for exploration. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 40, 2015 (2009)
M.S. Gilmore, J.W. Head, Sequential deformation of plains at the margins of Alpha Regio, Venus: implications for tessera formation. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 35, 667–687 (2000)
M.S. Gilmore, M.A. Ivanov, J.W. Head, A.T. Basilevsky, Duration of tessera deformation on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 13357–13368 (1997)
M.S. Gilmore, N. Mueller, J. Helbert, VIRTIS emissivity of Alpha Regio, Venus, with implications for tessera composition. Icarus 254, 350–361 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.04.008
B.J. Gladman, J.A. Burns, M. Duncan, P. Lee, H.F. Levinson, The exchange of impact ejecta between terrestrial planets. Science 271, 1387–1392 (1996)
T.D. Glotch et al., Highly silicic compositions on the Moon. Science 329, 1510–1513 (2010). 2013
R.E. Grimm, P.C. Hess, The crust of Venus, in Venus II, ed. by S.W. Bougher et al.(University of Arizona Press, Tuscon, 1997), pp. 1205–1244
D.H. Grinspoon, Implications of the high deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio for the sources of water in Venus’ atmosphere. Nature 363, 428–431 (1993)
D.H. Grinspoon, M.A. Bullock, Astrobiology and Venus exploration, in Exploring Venus as a Terrestrial Planet, ed. by L.W. Esposito et al.. AGU Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 176 (2007), pp. 191–206
J.P. Grotzinger, J.F. Kasting, New constraints on precambrian ocean composition. J. Geol. 101, 235–243 (1993)
J. Guandique, E. Kohler, V. Chevrier, Stability of metallic minerals under Venusian surface temperatures: investigating the potential source of radar anomalies. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 45, 2391 (2014)
J.E. Guest et al., Small volcanic edifices and volcanism in the plains of Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 97(E10), 15949–15966 (1992)
J.J. Hagerty, D.J. Lawrence, B.R. Hawke, D.T. Vaniman, R.C. Elphic, W.C. Feldman, Refined thorium abundances for lunar red spots: implications for evolved, non-mare volcanism on the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. 111, E06002 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JE002592
A.N. Halliday, The origins of volatiles in the terrestrial planets. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 105, 146–171 (2013)
E. Harrington, A.H. Treiman, The puzzle of radar-bright highlands on Venus: a high-spatial resolution study in Ovda Regio. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. XLVI, 2713 (2015)
G.A. Hashimoto, Y. Abe, Climate control on Venus: comparison of the carbonate and pyrite models. Planet. Space Sci. 53, 839–848 (2005)
G.L. Hashimoto, S. Sugita, On observing the compositional variability of the surface of Venus using nightside near-infrared thermal radiation. J. Geophys. Res. 108I, 5109 (2003). doi:10.1029/2003JE002082
G.A. Hashimoto, Y. Abe, S. Sasaki, CO2 amount on Venus constrained by a criterion of topographic-greenhouse instability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 289–292 (1997)
G.L. Hashimoto, M. Roos-Serote, S. Sugita, M.S. Gilmore, L.W. Kamp, R.W. Carlson, K.H. Baines, Felsic highland crust on Venus suggested by Galileo Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer data. J. Geophys. Res. 113, E00B24 (2008)
G.L. Hashimoto, M. Roos-Serote, S. Sugita, M.S. Gilmore, L.W. Kamp, R.W. Carlson, K.H. Baines, Felsic highland crust on Venus suggested by Galileo Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer data. J. Geophys. Res. 113, E00B24 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JE003134
R. Haus, G. Arnold, Radiative transfer in the atmosphere of Venus and application to surface emissivity retrieval from VIRTIS/VEX measurements. Planet. Space Sci. 58, 1578–1598 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.pss.2010.08.001
J.W. Head III., A.R. Peterfreund, J.B. Garvin, S.H. Zisk, Surface characteristics of Venus derived from Pioneer Venus altimetry, roughness, and reflectivity measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 6873–6885 (1985)
J. Helbert, A. Maturilli, The emissivity of a fine-grained labradorite sample at typical Mercury dayside temperatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 285, 347–354 (2009)
J. Helbert, N. Müller, P. Kostama, L. Marinangeli, G. Piccioni, P. Drossart, Surface brightness variations seen by VIRTIS on Venus Express and implications for the evolution of the Lada Terra region, Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L11201 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008GL033609
J. Helbert, S. Ferrari, A. Maturilli, M.D. Dyar, N. Müller, S. Smrekar, Studying the surface composition of Venus in the near infrared. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 46, 1793 (2015)
J. Helbert, A. Maturilli, M.D. Dyar, S. Ferrari, N. Müller, S. Smrekar, First set of laboratory Venus analog spectra for all atmospheric windows. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 48, 1512 (2017)
R.R. Herrick, Resurfacing history of Venus. Geology 22, 703–706 (1994). doi:10.1130/0091-7613
R.R. Herrick, M.E. Rumpf, Postimpact modification by volcanic or tectonic processes as the rule, not the exception, for Venusian craters. J. Geophys. Res. 116, E02004 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JE003722
R.R. Herrick, V.L. Sharpton, Implications from stereo-derived topography of Venusian impact craters. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 20245–20262 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999JE001225
Y. Hong, B. Fegley Jr., The kinetics and mechanism of pyrite thermal decomposition. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 101, 1870–1881 (1997)
Y. Hong, B. Fegley Jr., The sulfur vapor pressure over pyrite on the surface of Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 46, 683–690 (1998)
J.M. Hughes, J. Rakovan, The crystal structure of apatite, Ca5(PO4)3(F, OH, Cl). Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 48, 1–12 (2002)
G.R. Hunt, J.W. Salisbury, Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: I silicate minerals. Mod. Geol. 1, 283–300 (1970)
M.A. Ivanov, Morphology of the tessera terrain on Venus: implications for the composition of tessera material. Sol. Syst. Res. 35, 1–17 (2001)
M.A. Ivanov, A.T. Basilevsky, Density and morphology of impact craters on tesserae terrain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 2579–2582 (1993)
M.A. Ivanov, J.W. Head III, Geologic map of the Mylitta Fluctus quadrangle (V-61), Venus. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 2920 (2006)
M.A. Ivanov, J.W. Head, The history of volcanism on Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 84, 66–92 (2013)
N.R. Izenberg, R.E. Arvidson, R.J. Phillips, Impact crater degradation on Venusian plains. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21(4), 289–292 (1994). doi:10.1029/94GL00080
N.M. Johnson, B. Fegley Jr., Water on Venus: new insights from tremolite decomposition. Icarus 146, 301–306 (2000)
N.M. Johnson, B. Fegley Jr., Experimental studies of atmosphere-surface interactions on Venus. Adv. Space Res. 29, 233–241 (2002)
N.M. Johnson, B. Fegley Jr., Tremolite decomposition on Venus II. Products, kinetics, and mechanism. Icarus 164, 317–333 (2003a)
N.M. Johnson, B. Fegley Jr., Longevity of fluorine-bearing tremolite on Venus. Icarus 165, 340–348 (2003b)
D. Kappel, G. Arnold, R. Haus, Multi-spectrum retrieval of Venus IR surface emissivity maps from VIRTIS/VES nightside measurements at Themis Regio. Icarus 265, 42–62 (2016)
J.F. Kasting, J.B. Pollack, Loss of water from Venus, I, hydrodynamic escape of hydrogen. Icarus 63, 479–508 (1983)
W.M. Kaula, Constraints on Venus evolution from radiogenic argon. Icarus 139, 32–39 (1999)
K.B. Klose, J.A. Wood, A. Hashimoto, Mineral equilibria and the high radar reflectivity of Venus mountaintops. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 97, 16353–16369 (1992)
E. Kohler, V.F. Chevrier, P. Gavin, N. Johnson, Experimental investigation into the radar anomalies on the surface of Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 43, 2749 (2012)
E. Kohler, V.F. Chevrier, P. Gavin, N. Johnson, Experimental stability of tellurium and its implications for the Venusian radar anomalies. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 44, 2951 (2013)
E. Kohler et al., Proposed radar reflective minerals tested under Venus surface and atmosphere conditions. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 45, 2321 (2014)
E. Kohler, S. Port, V. Chevrier, N. Johnson, C. Lacy, Radar-reflective minerals investigated under Venus near-surface conditions. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 45, 2321 (2015)
V.A. Krasnopolsky, Spatially-resolved high-resolution spectroscopy of Venus 2. Variations of HDO, OCS and SO2 at the cloud tops. Icarus 209, 314–322 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2010.05.008
P.S. Kumar, J.W. Head, Geologic map of the Lada Terra quadrangle (V-56). Venus: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3249, scale 1:5,000,000 (2013), 11 p. doi:10.3133/sim3249
S. Kumar, H.A. Taylor Jr., Deuterium on Venus: model comparisons with Pioneer Venus observations of the predawn bulge atmosphere. Icarus 62, 494–504 (1984)
S.B. Lang, S.A.M. Tofail, A.L. Kholkin, M. Wojtas, M. Gregor, A.A. Gandhi, Y. Wang, S. Bauer, M. Krause, A. Plecenik, Ferroelectric polarization in nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite thin films on silicon. Sci. Rep. 3, 2215 (2013)
B.I. Lazoryak, V.A. Morozov, A.A. Belik, S.Yu. Stefanovich, V.V. Grebenev, I.A. Leonidov, E.B. Mitberge, S.A. Davydov, O.I. Lebedev, G. Van Tendeloo, Ferroelectric phase transition in the whitlockite-type Ca9Fe(PO4)7; crystal structure of the paraelectric phase at 923 K. Solid State Sci. 6, 185–195 (2004)
J. Lecacheux, P. Drossart, P. Laques, F. Deladerriere, F. Colas, Detection of the surface of Venus at 1.0 μm from ground-based observations. Planet. Space Sci. 41, 543–549 (1993)
C.-T.A. Lee, P. Luffi, T. Plank, H. Dalton, W.P. Leeman, Constraints on the depths and temperatures of basaltic magma generation on Earth and other terrestrial planets using new thermobarometers for mafic magmas. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 279(1–2), 20–33 (2009)
J.S. Lewis, An estimate of the surface conditions of Venus. Icarus 8, 434–456 (1968)
J.S. Lewis, Venus: atmospheric and lithospheric composition. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 10, 73–80 (1970)
K.P. Magee, J.W. Head, The role of rifting in the generation of melt: implications for the origin and evolution of the Lada Terra-Lavinia Planitia region of Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 1527–1552 (1995)
E. Marcq, J.-L. Bertaux, F. Montmessin, D. Belyaev, Variations of sulphur dioxide at the cloud top of Venus’s dynamic atmosphere. Nat. Geosci. 6, 25–28 (2013)
H.R.H. Martin, R. Smithies, J–F. Rapp Moyen, D. Champion, An overview of adakite, tonalite–trondhjemite–granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos 79, 1–24 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048
H. Masursky, E. Eliason, P.G. Ford, G.E. McGill, G.H. Pettengill, G.G. Schaber, G. Schubert, Pioneer-Venus radar results: geology from images and altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 8232–8260 (1980)
A. Maturilli, J. Helbert, J.M.St. John, J.W. Head III., W.M. Vaughan, M. D’Amore, M. Fottschalk, S. Ferrari, Komatiites as Mercury surface analogues: spectral measurements at PEL. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 398, 58–65 (2014)
M.C. McCanta, M.D. Dyar, A.H. Treiman, Alteration of Hawaiian basalts under sulfur-rich conditions: applications to understanding surface-atmosphere interactions on Mars and Venus. Am. Mineral. 99, 291–302 (2014)
W.B. McKinnon, K.J. Zahnle, B.I. Ivanov, H.J. Melosh, Cratering on Venus: models and observations, in Venus II, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Phillips (University of Arizona Press, Tuscon, 1997), pp. 969–1014
V.S. Meadows, D. Crisp, Ground-based near-infrared observations of the Venus nightside: the thermal structure and water abundance near the surface. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 4595–4622 (1996)
R.E. Milliken et al., Opaline silica in young deposits on Mars. Geology 36, 847–850 (2008)
H.J. Moore, J.J. Plaut, P.M. Schenk, J.W. Head, An unusual volcano on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 13479–13493 (1992)
A. Morbidelli et al., Building terrestrial planets. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 40, 251–275 (2012)
R.F. Mueller, Sources of HCl and HF in the atmosphere of Venus. Nature 220, 55–57 (1968)
R.F. Mueller, Planetary problems: origin of Venus atmosphere. Science 163, 1322–1324 (1969)
N. Mueller, J. Helbert, G.L. Hashimoto, C.C.C. Tsang, S. Erard, G. Piccolini, P. Drossart, Venus surface thermal emission at 1 mm in VIRTIS imaging observations: evidence for variation of crust and mantle differentiation conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 113, E00B17 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JE003118
O.V. Nikolayeva, M.A. Ivanov, V.K. Borozdin, Evidence on the crustal dichotomy, in Venus Geology, Geochemistry, and Geophysics, Research Results from the USSR, ed. by V.L. Barsukov, A.T. Basilevsky, V.P. Volkov, V.N. Zharkov (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992), pp. 129–139
J.G. O’Rourke, J. Korenaga, Terrestrial planet evolution in the stagnant lid regime: size effects and the formation of self-destabilizing crust. Icarus 221, 1043–1060 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2012.10.015
J.G. O’Rourke, A.S. Wolf, B.L. Ehlmann Venus, Interpreting the spatial distribution of volcanically modified craters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41 8252–8260 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014GL062121
E.M. Parmentier, P.C. Hess, Chemical differentiation of a convecting planetary interior: consequences for a one plate planet such as Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 2015–2018 (1992)
B. Pavri, J.W. Head III., K.B. Klose, L. Wilson, Steep-sided domes on Venus: characteristics, geologic setting, and eruption conditions from Magellan data. J. Geophys. Res. 97(E8), 13445–13478 (1992)
G.H. Pettengill, E. Eliason, P.G. Ford, G.B. Loriot, H. Masursky, G.E. McGill, Pioneer-Venus radar results: altimetry and surface properties. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 8261–8270 (1980)
G.H. Pettengill, P.G. Ford, B.D. Chapman, Venus: surface electromagnetic properties. J. Geophys. Res. 93(B12), 14881–14892 (1988)
G.H. Pettengill, P.G. Ford, R.J. Wilt, Venus surface radiothermal emission as observed by Magellan. J. Geophysics Res. 97(E8), 13091–13102 (1992)
G.H. Pettengill, P.G. Ford, R.A. Simpson, Electrical properties of the Venus surface from bistatic radar observations. Science 272, 1628–1631 (1996)
G.H. Pettengill, P.G. Ford, R.A. Simpson, Surface scattering and dielectric properties, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere, and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Philips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997), pp. 527–546
F.J. Pettijohn, P.E. Potter, R. Siever, Sand and Sandstone, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 1986)
R.J. Phillips, M.C. Malin, Tectonics of Venus. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 12, 411–443 (1984)
R.J. Phillips et al., Impact craters and Venus resurfacing history. J. Geophys. Res. 97(E10), 15923–15948 (1992)
C.M. Pieters, J.W. Head, S. Pratt, W. Patterson, J. Garvin, V.L. Barsukov, A.T. Basilevsky et al., The color of the surface of Venus. Science 234, 1379–1383 (1986)
S.T. Port, E. Kohler, V. Chevrier, Bismuth tellurides and sulfides mixtures and their relation to metal frost on Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 47, 2245 (2016)
S.T. Port, E. Kohler, V. Chevrier, Bismuth tellurides and sulfide mixtures and their relation to metal frost on Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 48, 1081 (2017)
R.G. Prinn, The photochemistry of the atmosphere of Venus, in The Photochemistry of Atmospheres, ed. by J.S. Levine (Academic Press, New York, 1985), pp. 281–336
B.G. Radoman-Shaw, R.P. Harvey, G.C.C. Costa, N.S. Jacobson, A. Avishai, L.M. Nakley, The stability of calcium silicates and calcium carbonate in the surface of Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 48, 2701 (2017)
E.O. Rausch, Dielectric properties of chlorapatite. Doctoral Dissertation, School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, 1976
K.M. Roberts, J.E. Guest, J.W. Head, M.G. Lancaster, Mylitta Fluctus, Venus: rift-related, centralized volcanism and the emplacement of large-volume flow units. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 15,991–16,015 (1992)
A.D. Rogers, H. Nekvasil, Feldspathic rocks on Mars: compositional constraints from infrared spectroscopy and possible formation mechanisms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42(8), 2619–2626 (2015)
I. Romeo, Monte Carlo models of the interaction between impact cratering and volcanic resurfacing on Venus: the effect of the Beta-Atla-Themis anomaly. Planet. Space Sci. 87, 157–172 (2013)
I. Romeo, R. Capote, Tectonic evolution of Ovda Regio: an example of highly deformed continental crust on Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 1428–1445 (2011)
I. Romeo, D.L. Turcotte, Pulsating continents on Venus: an explanation for crustal plateaus and tessera terrains. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 276, 85–97 (2008)
G.G. Schaber et al., Geology and distribution of impact craters on Venus: What are they telling us? J. Geophys. Res. 97(E8), 13257–13302 (1992)
L. Schaefer, B. Fegley Jr., Atmospheric chemistry of Venus-like exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 729, 6 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/729/1/6
A. Seiff, J.T. Schofield, A.J. Kliore, F.W. Taylor, S.S. Limaye, H.E. Revercomb, L.A. Sromovsky, V.V. Kerzhanovich, V.I. Moroz, M.Ya. Marov, Models of the structure of the atmosphere of Venus from the surface to 100 kilometers altitude. Adv. Space Res. 5, 3–58 (1985)
E.V. Shalygin, W.J. Markiewicz, A.T. Basilevsky, D.V. Titov, N.I. Ignatiev, J.W. Head, Active volcanism on Venus in the Ganiki Chasma rift zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 4762–4769 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL064088
J.G. Shellnutt, Petrological modeling of basaltic rocks from Venus: a case for the presence of silicic rocks. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 118(6), 1350–1364 (2013)
J.G. Shellnutt, Mantle potential temperature estimates of basalt from the surface of Venus. Icarus 277, 98–102 (2016)
M.K. Shepard, R.E. Arvidson, R.A. Brackett, B. Fegley, A ferroelectric model for the low emissivity highlands on Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21(6), 469–472 (1994)
Y.G. Shkuratov, M.A. Kreslavskii, O.V. Nikolaeva, Albedo-color diagram of the Venusian surface and its interpretation. Sol. Syst. Res. 21(2), 152–164 (1987)
Y.I. Sidorov, Mathematical simulation of complex natural systems. Geochem. Int. 44(1), 94–107 (2006)
R.A. Simpson, G.L. Tyler, B. Häusler, R. Mattei, M. Pätzold, Venus Express bistatic radar: high-elevation anomalous reflectivity. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 114(9), E00B41 (2009)
S.E. Smrekar, L. Elkins-Tanton, J.J. Leitner, A. Lenardic, S. Mackwell, L. Moresi, C. Sotin, E.R. Stofan, Tectonic and volcanic evolution of Venus and the role of volatiles: implications for understanding the terrestrial planets, in Exploring Venus as a Terrestrial Planet, ed. by L.W. Esposito et al.. AGU Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 176 (2007), pp. 45–71
S.E. Smrekar, E.R. Stofan, N. Mueller, A. Treiman, L. Elkins-Tanton, J. Helbert, G. Piccolini, P. Drossart, Recent hotspot volcanism on Venus from VIRTIS emissivity data. Science 328, 605–608 (2010). doi:10.1126/science.1186785
S.E. Smrekar, E.R. Stofan, N. Mueller, Venus: surface and interior, in Encyclopedia of the Solar System, ed. by T. Spohn, D. Breuer, T.V. Johnson (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014), pp. 323–341
V.S. Solomatov, L–N. Moresi, Stagnant lid convection on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 4737–4753 (1996)
S.C. Solomon, A tectonic resurfacing model for Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 24, 1331 (1993)
S.D. Spulber, M.J. Rutherford, The origin of rhyolite and plagiogranite in oceanic crust: an experimental study. J. Petrol. 24, 1–25 (1983)
E.R. Stofan et al., Global distribution and characteristics of coronae and related features on Venus: implications for origin and relation to mantle processes. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 13347–13378 (1992)
P.H. Stone, The dynamics of the atmosphere of Venus. J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 1005–1016 (1975)
B.L. Straley, M.S. Gilmore, Mapping and structural analysis of SW Tellus Regio, Venus. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 38, 1657 (2007)
R.G. Strom, G.G. Schaber, D.D. Dawson, The global resurfacing of Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 10899–10926 (1994)
T. Sweetser, J. Cameron, G-S. Chen, J. Cutts, R. Gershmann, M.S. Gilmore, J. Hall, V. Kerzhanovich, A. McRonald, E. Nilsen, W. Petrick, D. Rodgers, B. Wilcox, A. Yavrouian, W. Zimmerman, JPL Advanced Projects Design Team, Venus surface sample return: a weighty high-pressure challenge. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 103(3), 831–844 (2000). Proc. AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Conf., Aug. 16–19, 1999, Girdwood, Alaska
F.W. Taylor, Climate variability on Venus and Titan. Space Sci. Rev. 125, 445–455 (2006)
F.W. Taylor, D. Crisp, B. Bézard, Near-infrared sounding of the lower atmosphere of Venus, in Venus II, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R. Phillips (University of Arizona Press, Tuscon, 1997), pp. 325–351
K.L. Tanaka, D.A. Senske, M. Price, R.L. Kirk, Physiography, geomorphic/geologic mapping and stratigraphy of Venus, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere, and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher et al.(University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997), pp. 667–694
A.H. Treiman, Geochemistry of Venus’ surface: current limitations as future opportunities, in Exploring Venus as a Terrestrial Planet, ed. by L.W. Esposito, E.R. Stofan, T.E. Cravens. AGU Monograph Series, vol. 176 (2007), pp. 7–22
A.H. Treiman, C.C. Allen, Chemical weathering on Venus: preliminary results on the interaction of basalt and CO2. Lunar Planet. Sci. XXV, 1415–1416 (1994)
A.H. Treiman, M.A. Bullock, Mineral reaction buffering of Venus’ atmosphere: a thermochemical constraint and implications for Venus-like planets. Icarus 217, 534–541 (2012)
A.H. Treiman, S.P. Schwenzer, Basalt–atmosphere interaction on Venus: preliminary results on weathering of minerals and bulk rock, in Venus Geochemistry: Progress, Prospects, and New Missions, Abstract #2011 (2009)
A. Treiman, E. Harrington, V. Sharpton, Venus’ radar bright highlands: different signatures and materials on Ovda Regio and on Maxwell Montes. Icarus 280, 172–182 (2016)
C.C.C. Tsang, P.G.J. Irwin, F.W. Taylor, C.F. Wilson, A correlated-k model of radiative transfer in the near-infrared windows of Venus. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 109, 1118–1135 (2008)
M.E. Tucker, V.P. Wright, Carbonate Sedimentology (Blackwell, Oxford, 1990), 496 pp.
D.L. Turcotte, G. Morein, D. Roberts, B.D. Malamud, Catastrophic resurfacing and episodic subduction on Venus. Icarus 139, 49–54 (1999)
G.L. Tyler et al., Magellan: electrical and physical properties of Venus’ surface. Science 252, 265–270 (1991)
H.C. Urey, The Planets (Yale University Press, New Haven, 1952)
VEXAG, Technology Plan (2014). http://www.lpi.usra.edu/vexag/reports/Venus-Technology-Plan-140617.pdf
V.P. Volkov, M.Yu. Zolotov, I.L. Khodakovsky, Lithospheric-atmospheric interaction on Venus, in Chemistry and Physics of the Terrestrial Planets, ed. by S.K. Savena (Springer, New York, 1986), pp. 136–190
M.J. Way et al., Was Venus the first habitable world of our solar system? Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 8376–8383 (2016)
J.J. Wray et al., Prolonged magmatic activity on Mars inferred from the detection of felsic rocks. Nat. Geosci. 6, 1013–1017 (2013)
C.M. Weitz, A.T. Basilevsky, Magellan observations of the Venera and Vega landing site regions. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 17069–17097 (1993)
M. Weller, M. Duncan, Insight into terrestrial planetary evolution via mantle potential temperatures. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. Abstr. 46, 2749 (2015)
M. Whitaker, H. Nekvasil, D.H. Lindsley, Potential magmatic diversity on Mars. Lunar Planet. Sci. 36, 1440 (2005)
J.L. Whitten, B.A. Campbell, Recent volcanic resurfacing of Venusian craters. Geology (2016). doi:10.1130/G37681.1
J.A. Wood, Rock weathering on the surface of Venus, in Venus II: Geology, Geophysics, Atmosphere and Solar Wind Environment, ed. by S.W. Bougher, D.M. Hunten, R.J. Philips (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997), pp. 637–664
J.A. Wood, R. Brett, Comment on “The rate of pyrite decomposition on the surface of Venus”. Icarus 128, 472–473 (1997)
Y. Yamanoi, S. Nakashima, M. Katsura, Temperature dependence of reflectance spectra and color values of hematite by in situ, high-temperature visible micro-spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 94, 90–97 (2009)
M.Y. Zolotov, A model of thermochemical equilibrium in the near-surface atmosphere of Venus. Geochem. Int. 11, 80–100 (1996)
M.Yu. Zolotov, Solid planet-atmosphere interactions, in Treatise on Geophysics, vol. 10, ed. by G. Schubert (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2007), pp. 349–369
M.Y. Zolotov, I.L. Khodakovsky, Exogenic processes, in The Planet Venus: Atmosphere, Surface, Interior Structure, ed. by Y.L. Barsukov, Y. Volkov (Nauka, Moscow, 1989), pp. 262–290
M.Y. Zolotov, B. Fegley Jr., K. Lodders, Hydrous silicates and water on Venus. Icarus 130(2), 475–494 (1997)
M.Y. Zolotov, B. Fegley Jr., K. Lodders, Stability of micas on the surface of Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 47, 245–260 (1999)
Acknowledgements
We appreciate discussions with Justin Filiberto, John Grotzinger, and Bruce Fegley. We thank the reviewers who provided very helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Venus III
Edited by Bruno Bézard, Christopher T. Russell, Takehiko Satoh, Suzanne E. Smrekar and Colin F. Wilson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilmore, M., Treiman, A., Helbert, J. et al. Venus Surface Composition Constrained by Observation and Experiment. Space Sci Rev 212, 1511–1540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0370-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0370-8