Abstract
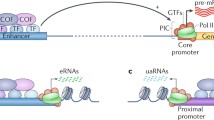
Specific transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II at eukaryotic protein-coding genes involves the cooperative assembly at the core promoter of more than 40 distinct proteins – with a total mass of over 2 MDa – including RNA polymerase II itself and general/basal transcription initiation factors, to form a stable pre-initiation complex (PIC). In vivo, PIC assembly is a major point of regulation by sequence-specific transcription regulators (activators and repressors) and is hindered by the packaging of promoter DNA into nucleosomes and higher order chromatin structures. Genetic and biochemical studies have recently identified a variety of transcription cofactors/co-regulators (coactivators and corepressors) that interact with sequence-specific regulators and/or various components of the general/basal transcription machinery and are essential for regulated transcription. An emerging view from these studies is that regulators must target two types of transcription cofactors: chromatin-modifying/remodeling cofactors and general cofactors that associate with and/or influence the activities of components of the general/basal transcription machinery. The recent biochemical identification and characterization of many different chromatin-modifying and general transcription cofactors has revealed their often complex multi-subunit nature and a previously unsuspected level of structural and functional redundancy. Another emerging theme is the multifunctional nature of chromatin-modifying cofactor complexes that appear to couple gene-specific transcription to other cellular processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abmayr, S.M., Workman, J.L. and Roeder, R.G. 1988. The pseudorabies immediate early [protein stimulates in vitro transcription by facilitating TFIID: promoter interactions. Genes Dev. 2: 542–553.
Allard, S., Utley, R.T., Savard, J., Clarke, A., Grant, P., Brandl, C.J., Pillus, L., Workman, J.L. and Cote, J. 1999. EMBO J. 18: 5108–5119.
Apone, L.M., Virbasius, C.M., Reese, J.C. and Green, M.R. 1996. Yeast TAF(II)90 is required for cell-cycle progression through G2/M but not for general transcription activation. Genes Dev. 10: 2368–2380.
Baldwin, D.A. and Gurley, W.B. 1996. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding transcription factor IIB from Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant J. 10: 561–568.
Belotserkovskaya, R., Sterner, D.E., Deng, M., Sayre, M.H, Lieberman, P.M. and Berger, S.L. 2000. Inhibition of TATA-binding protein function by SAGA subunits Spt3 and Spt8 at Gcn4-activated promoters. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 634–647.
Berger, S.L. 2001. The histone modification circus. Science 292: 64–65.
Berk, A.J. 2000. TBP-like factors come into focus. Cell 103: 5–8.
Bhaumik, S.R. and Green, M.R. 2001. SAGA is an essential in vivo target of the yeast acidic activator Gal4p. Genes Dev. 15: 1935–1945.
Björklund, S., Almouzni, G., Davidson, I., Nightingale, K.P. and Weiss, K. 1999. Global transcription regulators of eukaryotes. Cell 96: 759–767.
Brand, M., Yamamoto, K., Staub, A. and Tora, L. 1999. Identification of TATA-binding protein-free TAFII-containing complex subunits suggests a role in nucleosome acetylation and signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 18285–18289.
Brand, M., Moggs, J.G., Oulad-Abdelghani, M., Lejeune, F., Dilworth, F.J., Stevenin, J., Almouzni, G. and Tora, L. 2001. UV-damaged DNA-binding protein in the TFTC complex links DNA damage recognition to nucleosome acetylation. EMBO J. 20: 3187–3196.
Brown, C.E., Lechner, T., Howe, L. and Workman, J.L. 2000. The many HATs of transcription coactivators. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 15–19.
Brzeski, J., Podstolski, W., Olczak, K. and Jerzmanowski, A. 1999. Identification and analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana BSH gene, a member of the SNF5 gene family. Nucl. Acids Res. 27: 2393–2399.
Burke, L.J. and Baniahmad, A. 2000. Co-repressors 2000. FASEB J. 14: 1876–1888.
Burke, T.W. and Kadonaga, J.T. 1996. Drosophila TFIID binds to a conserved downstream basal promoter element that is present in many TATA-box-deficient promoters. Genes Dev. 10: 711–724.
Burke, T.W. and Kadonaga, J.T. 1997. The downstream core promoter element, DPE, is conserved from Drosophila to humans and is recognized by TAFII60 of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 11: 3020–3031.
Burley, S.K. and Roeder, R.G. 1996. Biochemistry and structural biology of transcription (factor IID (TFIID). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65: 769–799.
Carey, M. 1998. The enhanceosome and transcriptional synergy. Cell 92: 5–8.
Castaño, E., Gross, P., Wang, Z., Roeder, R.G. and Oelgeschläger, T. 2000. The C-terminal domain-phosphorylated IIO form of RNA polymerase II is associated with the transcription repressor NC2 (Dr1/DRAP1) and is required for transcription activation in human nuclear extracts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 7184–7189.
Chalkley, G.E. and Verrijzer, C.P. 1999. DNA binding site selection by RNA polymerase II TAFs: a TAF(II)250-TAF(II) 150 complex recognizes the initiator. EMBO J. 18: 4835–4845.
Chang, W.H. and Kornberg, R.D. 2000. Electron crystal structure of the transcription factor and DNA repair complex, core TFIIH. Cell 102: 609–613.
Chen, Z. and Manley, J.L. 2000. Robust mRNA transcription in chicken DT40 cells depleted of TAF(II)31 suggests both functional degeneracy and evolutionary divergence. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 5064–5076.
Chen, J.L., Attardi, L.D., Verrijzer, C.P., Yokomori, K. and Tjian, R. 1994. Assembly of recombinant TFIID reveals differential coactivator requirements for distinct transcriptional activators. Cell 79: 93–105.
Chen, D., Ma, H., Hong, H., Koh, S.S., Huang, S.M., Schurter, B.T., Aswad, D.W. and Stallcup, M.R. 1999. Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase. Science L 284: 2174–2177.
Chi, T. and Carey, M. 1996. Assembly of the isomerized TFIIA-TFIID-TATA ternary complex is necessary and sufficient for gene activation. Genes Dev. 10: 2540–2550.
Chi, T., Lieberman, P., Ellwood, K. and Carey, M. 1995. A general mechanism for transcriptional synergy by eukaryotic activators. Nature 377: 254–257.
Chi, Y., Huddleston, M.J., Zhang, X., Young, R.A., Annan, R.S., Carr, S.A., Deshaies, R.J. 2001. Negative regulation of Gcn4 and Msn2 transcription factors by Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinase. Genes Dev. 15: 1078–1092.
Chiang, C.M. and Roeder, R.G. 1995. Cloning of an intrinsic human TFIID subunit that interacts with multiple transcriptional activators. Science 267: 531–536.
Cosma, M.P., Tanaka, T. and Nasmyth, K. 1999. Ordered recruitment of transcription and chromatin remodeling factors to a cell cycle-and developmentally regulated promoter. Cell 97: 299–311.
Cramer, P., Bushnell, D.A. and Kornberg, R.D. 2001. Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 Å resolution. Science 292: 1863–1876.
Dantonel, J.C., Murthy, K.G., Manley, J.L. and Tora, L. 1997. Transcription factor TFIID recruits factor CPSF for formation of 3' end of mRNA. Nature 389: 399–402.
de Laat, W.L., Jaspers, N.G. and Hoeijmakers, J.H. 1999. Molecular mechanism of nucleotide excision repair. Genes Dev. 13: 768–785.
Dikstein, R., Ruppert, S. and Tjian, R. 1996. TAFII250 is a bipartite protein kinase that phosphorylates the base transcription factor RAP74. Cell 84: 781–790.
Dotson, M.R., Yuan, C.X., Roeder, R.G., Myers, L.C., Gustafsson, C.M., Jiang, Y.W., Li, Y., Kornberg, R.D. and Asturias, F.J. 2001. Structural organization of yeast and mammalian mediator complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 14307–14310.
Dudley, A.M., Rougeulle, C. and Winston, F. 1999. The Spt components of SAGA facilitate TBP binding to a promoter at a post-activator-binding step in vivo. Genes Dev. 13: 2940–2945.
Dvir, A., Conaway, J.W. and Conaway, R.C. 2001. Mechanism of transcription initiation and promoter escape by RNA polymerase II. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11: 209–214.
Eberharter, A., Sterner, D.E., Schieltz, D., Hassan, A., Yates, J.R. 3rd, Berger, S.L., Workman, J.L. 1999. The ADA complex is a distinct histone acetyltransferase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 6621–6631.
Eisenmann, D.M., Arndt, K.M., Ricupero, S.L., Rooney, J.W. and Winston, F. 1992. SPT3 interacts with TFIID to allow normal transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 6: 1319–1331.
Emami, K.H., Jain, A. and Smale, S.T. 1997. Mechanism of synergy between TATA and initiator: synergistic binding of TFIID following a putative TFIIA-induced isomerization. Genes Dev. 11: 3007–3019.
Eshed, Y., Baum, S.F. and Bowman J.L. 1999. Distinct mechanisms promote polarity establishment in carpels of Arabidopsis. Cell 99: 199–209.
Flanagan, P.M., Kelleher, R.J. 3rd, Sayre, M.H., Tschochner, H. and Kornberg, R.D. 1991. A mediator required for activation of RNA polymerase II transcription in vitro. Nature 350: 436–438.
Finnegan, E.J. 2001. Is plant gene expression regulated globally? Trends Genet. 17: 361–365.
Fondell, J.D., Guermah, M., Malik, S. and Roeder, R.G. 1999. Thyroid hormone receptor-associated proteins and general positive cofactors mediate thyroid hormone receptor function in the absence of the TATA box-binding protein-associated factors of TFIID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 1959–1964.
Fry, C.J. and Peterson, C.L. 2001. Chromatin remodeling enzymes: who's on first? Curr. Biol. 11: R185–R197.
Gangloff, Y.G., Werten, S., Romier, C., Carre, L., Poch, O., Moras, D. and Davidson, I. 2000. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 340–351.
Gangloff, Y.G., Pointud, J.C, Thuault, S., Carre, L., Romier, C., Muratoglu, S., Brand, M., Tora, L., Couderc, J.L. and Davidson, I. 2001. The TFIID components human TAFII140 and Drosophila BIP2 (TAFII155) are novel metazoan homologues of yeast TAFII47 containing a histone fold and a PHD finger. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 5109–5121.
Gasch, A., Hoffmann, A., Horikoshi, M., Roeder, R.G. and Chua, N.H. 1990. N.G. 1990. Arabidopsis thaliana contains two genes for TFIID. Nature 346: 390–394.
Ge, H. and Roeder, R.G. 1994. Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell 78: 513–523.
Geiger, J.H., Hahn, S., Lee, S. and Sigler, P.B. 1996. Crystal structure of the yeast TFIIA/TBP/DNA complex. Science 272: 830–836.
Geisberg, J.V., Holstege, F.C., Young, R.A. and Struhl, K. 2001. Yeast NC2 associates with the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex and selectively affects transcription in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 2736–2742.
Gnatt, A.L., Cramer, P., Fu, J., Bushnell, D.A. and Kornberg, R.D. 2001. Structural basis of transcription: an RNA polymerase II elongation complex at 3.3 Å resolution. Science 292: 1876–1882.
Grant, P.A. 2001. A tale of histone modifications. Genome Biol. 2: reviews0003.1-0003.6
Grant, P.A., Duggan, L., Cote, J., Roberts, S.M., Brownell, J.E., Candau, R., Ohba, R., Owen-Hughes, T., Allis, C.D., Winston, F., Berger, S.L. and Workman, J.L. 1997. Yeast Gcn5 functions in two multisubunit complexes to acetylate nucleosomal histones: characterization of an Ada complex and the SAGA (Spt/Ada) complex. Genes Dev. 11: 1640–1650.
Grant, P.A., Schieltz, D., Pray-Grant, M.G., Steger, D.J., Reese, J.C., Yates, J.R. III and Workman, J.L. 1998a. A subset of TAF(II)s are integral components of the SAGA complex required for nucleosome acetylation and transcriptional stimulation. Cell 94: 45–53.
Grant, P.A., Schieltz, D., Pray-Grant, M.G., Yates, J.R. III and Workman, J.L. 1998b. The ATM-related cofactor Tra1 is a component of the purified SAGA complex. Mol. Cell 2: 863–867.
Green, M.R. 2000. TBP-associated factors (TAFIIS ): multiple, selective transcriptional mediators in common complexes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 59–63.
Hampsey, M. 1998. Molecular genetics of the RNA polymerase II general transcription machinery. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62: 465–503.
Hansen, S.K. and Tjian, R. 1995. TAFs and TFIIA mediate differential utilization of the tandem Adh promoters. Cell 82: 565–575.
Hassan, A.H., Neely, K.E. and Workman, J.L. 2001. Histone acetyltransferase complexes stabilize swi/snf binding to promoter nucleosomes. Cell 104: 817–827.
Hoeijmakers, J.H., Egly,, J.M. and Vermeulen, W. 1996. TFIIH: a key component in multiple DNA transactions. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6: 26–33.
Hoey, T., Dynlacht, B.D., Peterson, M.G., Pugh, B.F. and Tjian, R. 1990. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila gene encoding the TATA box binding protein, TFIID. Cell 61: 1179–1186.
Hoffmann, A., Sinn, E., Yamamoto, T., Wang, J., Roy, A., Horikoshi, M. and Roeder, R.G. 1990. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature 346: 387–390.
Hoffmann, A., Chiang, C.M., Oelgeschläger, T., Xie, X., Burley, S.K., Nakatani, Y. and Roeder, R.G. 1996. A histone octamer-like structure within TFIID. Nature 380: 356–359.
Hoffmann, A., Oelgeschläger, T. and Roeder, R.G. 1997. Considerations of Transcriptional control mechanisms: do TFIID-core promoter complexes recapitulate nucleosome-like functions? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 8928–8935.
Holmes, M.C. and Tjian, R. 2000. Promoter-selective properties of the TBP-related factor TRF1. Science 288: 867–870.
Holstege, F.C., Jennings, E.G., Wyrick, J.J., Lee, T.I., Hengartner, C.J., Green, M.R., Golub, T.R., Lander, E.S. and Young, R.A. 1998. Dissecting the regulatory circuitry of a eukaryotic genome. Cell 95: 717–728.
Horikoshi, M., Carey, M.F., Kakidani, H. and Roeder, RG. 1988a. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell 54: 665–669.
Horikoshi, M., Hai, T., Lin, Y.S., Green, M.R. and Roeder, R.G. 1988b. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell 54: 1033–1042.
Horiuchi, J., Silverman, N., Pina, B., Marcus, G.A. and Guarente, L. 1997. ADA1, a novel component of the ADA/GCN5 complex, has broader effects than GCN5, ADA2, or ADA3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 3220–3228.
Ikeda, K., Halle, J.P., Stelzer, G., Meisterernst, M. and Kawakami, K. 1998. Involvement of negative cofactor NC2 in active repression by zinc finger-homeodomain transcription factor AREB6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 10–18.
Ikeda, K., Steger, D.J., Eberharter, A. and Workman, J.L. 1999. Activation domain-specific and general transcription stimulation by native histone acetyltransferase complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 855–863.
Ikura, T., Ogryzko, V.V, Grigoriev, M., Groisman, R., Wang, J., Horikoshi, M., Scully, R., Qin, J. and Nakatani, Y. 2000. Involvement of the TIP60 histone acetylase complex in DNA repair and apoptosis. Cell 102: 463–473.
Imhof, A., Yang, X.J., Ogryzko, V.V., Nakatani, Y., Wolffe, A.P. and Ge, H. 1997. Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases. Curr. Biol. 7: 689–692.
Jacobson, R.H., Ladurner, A.G., King, D.S., Tjian, R. 2000. Structure and function of a human TAFII250 double bromodomain module. Science 288: 1422–1425.
Kaiser, K., Stelzer, G. and Meisterernst, M. 1995. The coactivator p15 (PC4) initiates transcriptional activation during TFIIATFIID-promoter complex formation. EMBO J. 14: 3520–3527.
Kamada, K., Shu, F., Chen, H., Malik, S., Stelzer, G., Roeder, R.G., Meisterernst, M., Burley, S.K. 2001. Crystal structure of negative cofactor 2 recognizing the TBP-DNA transcription complex. Cell 106: 71–81.
Kang, J.J., Auble, D.T., Ranish, J.A., Hahn, S. 1995. Analysis of the yeast transcription factor TFIIA: distinct functional regions and a polymerase II-specific role in basal and activated transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 1234–1243.
Kim, Y.J., Bjorklund, S., Li, Y., Sayre, M.H. and Kornberg, R.D. 1994. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell 77: 599–608.
Knoepfler, P.S. and Eisenman, R.N. 1999. Sin meets NuRD and other tails of repression. Cell 99: 447–450.
Kobayashi, N., Boyer, T.G. and Berk, A.J. 1995. A class of activation domains interacts directly with TFIIA and stimulates TFIIA-TFIID-promoter complex assembly. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 6465–6473.
Koleske, A.J. and Young, R.A. 1994. An RNA polymerase II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature 368: 466–469.
Kouzarides, T. 2000. Acetylation: a regulatory modification to riyal phosphorylation? EMBO J. 19: 1176–1179.
Kraemer, S.M., Ranallo, R.T., Ogg, R.C. and Stargell, L.A. 2001. TFIIA interacts with TFIID via association with TATA-binding protein and TAF40. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 1737–1746.
Krebs, J.E., Kuo, M.H., Allis, C.D., Peterson, C.L. 1999. Cell cycle-regulated histone acetylation required for expression of the yeast HO gene. Genes Dev. 13: 1412–1421.
Kretzschmar, M., Kaiser, K., Lottspeich, F. and Meisterernst, M. 1994. A novel mediator of class II gene transcription with homology to viral immediate-early transcriptional regulators. Cell 78: 525–534.
Kuo, M.H., Zhou, J., Jambeck, P., Churchill, M.E. and Allis, C.D. 1998. Histone acetyltransferase activity of yeast Gcn5p is required for the activation of target genes in vivo. Genes Dev. 12: 627–639.
Kuras, L., Kosa, P., Mencia, M. and Struhl, K. 2000. TAF-Containing and TAF-independent forms of transcriptionally active TBP in vivo. Science 288: 1244–1248.
Lagrange, T., Kapanidis, A.N., Tang, H., Reinberg D. and Ebright, R.H. 1998. New core promoter element in RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription: sequence-specific DNA binding by transcription factor IIB. Genes Dev. 12: 34–44.
Larkin, R.M., Hagen, G. and Guilfoyle T.J. 1999. Arabidopsis thaliana RNA polymerase II subunits related to yeast and human RPB5. Gene 231: 41–47.
Larschan, E. and Winston, F. 2001. The S. cerevisiae SAGA complex functions in vivo as a coactivator for transcriptional activation by Gal4. Genes Dev. 15: 1946–1956.
Lee, T.I., Causton, H.C., Holstege, FC., Shen, W.C., Hannett, N., Jennings, E.G., Winston, F., Green, M.R. and Young, R.A. 2000. Redundant roles for the TFIID and SAGA complexes in global transcription. Nature 405: 701–704.
Lemon, B. and Tjian, R. 2000. Orchestrated response: a symphony of transcription factors for gene control. Genes Dev. 14: 2551–2569.
Li, Y.F., Le Gourierrec, J., Torki, M., Kim, Y.J., Guerineau, F. and Zhou, D.X. 1999. Characterization and functional analysis of Arabidopsis. TFIIA reveal that the evolutionarily unconserved region of the large subunit has a transcription activation domain. Plant Mol. Biol. 39: 515–525.
Li, X.Y., Bhaumik, S.R. and Green, M.R. 2000. Distinct classes of yeast promoters revealed by differential TAF recruitment. Science 288: 1242–1244.
Lieberman, P.M. and Berk, A.J. 1994. A mechanism for TAFs in transcriptional activation: activation domain enhancement of TFIID-TFIIA-promoter DNA complex formation. Genes Dev. 8: 995–1006.
Liu, Y., Ranish, J.A., Aebersold, R. and Hahn, S. 2001. Yeast nuclear extract contains two major forms of RNA polymerase II mediator complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 7169–7175.
Lorch, Y., Beve, J., Gustafsson, C.M., Myers, L.C. and Kornberg, R.D. 2000. Mediator-nucleosome interaction. Mol. Cell 6: 197–201.
Malik, S. and Roeder, R.G. 2000. Transcriptional regulation through Mediator-like coactivators in yeast and metazoan cells. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 277–283.
Malik, S., Guermah, M. and Roeder, R.G. 1998. A dynamic model for PC4 coactivator function in RNA polymerase II transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 2192–2197.
Malik, S., Gu, W., Wu, W., Qin, J. and Roeder, R.G. 2000. The USA-derived transcriptional coactivator PC2 is a submodule of TRAP/SMCC and acts synergistically with other PCs. Mol. Cell 5: 753–760.
Martinez, E., Chiang, C.M., Ge, H. and Roeder, R.G. 1994. TATA-binding protein-associated factor(s) in TFIID function through the initiator to direct basal transcription from a TATA-less class II promoter. EMBO J. 13: 3115–3126.
Martinez, E., Zhou, Q., L'Etoile, N.D., Oelgeschläger, T., Berk, A.J. and Roeder, R.G. 1995. Core promoter-specific function of a mutant transcription factor TFIID defective in TATA-box binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 11864–11868.
Martinez, E., Ge, H., Tao, Y., Yuan, C.X., Palhan, V. and Roeder, R.G. 1998a. Novel cofactors and TFIIA mediate functional core promoter selectivity by the human TAFII150-containing TFIID complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 6571–6583.
Martinez, E., Kundu, T.K., Fu, J. and Roeder, R.G. 1998b. A human SPT3-TAFII31-GCN5-L acetylase complex distinct from transcription factor IID. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 23781–23785.
Martinez, E., Palhan, V.B., Tjernberg, A., Lymar, E.S., Gamper, A.M., Kundu, T.K., Chait, B.T. and Roeder, R.G. 2001. Human STAGA complex is a chromatin-acetylating transcription coactivator that interacts with pre-mRNA splicing and DNA damage-binding factors in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 6782–6795.
Matangkasombut, O., Buratowski, R.M., Swilling, N.W. and Buratowski, S. 2000. Bromodomain factor 1 corresponds to a missing piece of yeast TFIID. Genes Dev. 14: 951–962.
Merika, M. and Thanos, D. 2001. Enhanceosomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11: 205–208.
Metzger, D., Scheer, E., Soldatov, A. and Tora, L. 1999. Mammalian TAF(II)30 is required for cell cycle progression and specific cellular differentiation programmes. L EMBO J. 18: 4823–4834.
Mizuguchi, G., Vassilev, A., Tsukiyama, T., Nakatani, Y. and Wu, C. 2001. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling and histone hyperacetylation synergistically facilitate transcription of chromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 14773–14783
Mizzen, C.A., Yang, X.J., Kokubo, T., Brownell, J.E., Bannister, A.J., Owen-Hughes, T., Workman, J., Wang, L., Berger, S.L., Kouzarides, T., Nakatani, Y. and Allis, C.D. 1996. The TAF(II)250 subunit of TFIID has histone acetyltransferase activity. Cell 87: 1261–1270.
Moqtaderi, Z., Bai, Y., Poon, D., Weil, P.A. and Struhl, K. 1996. TBP-associated factors are not generally required for transcriptional activation in yeast. Nature 383: 188–191.
Murfett, J., Wang, X.J., Hagen, G. and Guilfoyle, T.J. 2001. Identification of arabidopsis histone deacetylase hda6 mutants that affect transgene expression. Plant Cell 13: 1047–1061.
Myers, L.C. and Kornberg, R.D. 2000. Mediator of transcriptional regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 729–749.
Näär, A.M., Beaurang, P.A., Robinson, K.M., Oliner, J.D., Avizonis, D., Scheek, S., Zwicker, J., Kadonaga, J.T. and Tjian, R. 1998. Chromatin, TAFs, and a novel multiprotein coactivator are required for synergistic activation by Sp1 and SREBP-1a in vitro. Genes Dev. 12: 3020–3031.
Näär, A.M., Lemon, B.D., Tjian, R. 2001. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70: 475–501.
Ng, H.H. and Bird, A. 2000. Histone deacetylases: silencers for hire. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 121–126.
Nielsen, S.J., Schneider, R., Bauer, V.M., Bannister, A.J., Morrison, A., O'Carroll, D., Firestein, R., Cleary, M., Jenuwein, T., Herrera, R.E. and Kouzarides, T. 2001. Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 412: 561–565.
Nikolov, D.B., Chen, H., Halay, E.D., Usheva, A.A., Hisatake, K., Lee, D.K., Roeder, R.G., Burley, S.K. 1995. Crystal structure of a TFIIB-TBP-TATA-element ternary complex. Nature 377: 119–128.
Nogales, E. 2000. Recent structural insights into transcription preinitiation complexes. J. Cell. Sci. 113: 4391–4397.
O'Brien, T. and Tjian, R. 2000. Different functional domains of TAFII250 modulate expression of distinct subsets of mammalian genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 2456–2461.
Oelgeschläger, T., Chiang, C.M. and Roeder, R.G. 1996. Topology and reorganization of human TFIID-promoter complex. Nature 382: 735–738.
Oelgeschläger T., Tao, Y., Kang, Y.K. and Roeder, R.G. 1998. Transcription activation via enhanced preinitiation complex assembly in a human cell-free system lacking TAFII S. Mol. Cell. 1: 925–9
Ogas, J., Kaufmann, S., Henderson, J. and Somerville, C. 1999. PICKLE is a CHD3 chromatin-remodeling factor that regulates the transition from embryonic to vegetative development in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 13839–13844.
Ogryzko, V.V., Kotani, T., Zhang, X., Schiltz, R.L., Howard, T., Yang, X.J., Howard, B.H., Qin, J. and Nakatani, Y. 1998. Histone-like TAFs within the PCAF histone acetylase complex. Cell 94: 35–44.
Orphanides, G., Lagrange T. and Reinberg, D. 1996. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 10: 2657–2683.
Ozer, J., Moore, P.A., Bolden, A.H., Lee, A., Rosen, C.A. and Lieberman, P.M. 1994. Molecular cloning of the small (gamma) subunit of human TFIIA reveals functions critical for activated transcription. Genes Dev. 8: 2324–2335.
Ozer, J., Mitsouras, K., Zerby, D., Carey, M. and Lieberman, P.M. 1998a. Transcription factor IIA derepresses TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor inhibition of TBP-DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 14293–14300.
Ozer, J., Lezina, L.E., Ewing, J., Audi S. and Lieberman, P.M. 1998b. Association of transcription factor IIA with TATA binding protein is required for transcriptional activation of a subset of promoters and cell cycle progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 2559–2570.
Ozer, J., Moore, P.A. and Lieberman, P.M. 2000. A testis-specific transcription factor IIA (TFIIAtau) stimulates TATA-binding protein-DNA binding and transcription activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 122–128.
Park, J.M., Gim, B.S., Kim, J.M., Yoon, J.H., Kim, H.S., Kang, J.G. and Kim, Y.J. 2001. Drosophila Mediator complex is broadly utilized by diverse gene-specific transcription factors at different types of core promoters. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 2312–2323.
Patikoglou, G. and Burley, S.K. 1997. Eukaryotic transcription factor-DNA complexes. Annu. Rev. Biomol. Struct. 26: 289–325.
Pham, A.D. and Sauer, F. 2000. Ubiquitin-activating/conjugating activity of TAFII250, a mediator of activation of gene expression in Drosophila. Science 289: 2357–2360.
Pugh, B.F. and Tjian, R. 1990. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell 61: 1187–1197.
Pugh, B.F. and Tjian, R. 1991. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 5: 1935–1945.
Roeder, R.G. 1996. The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21: 327–335.
Roeder, R.G. 1998. Role of general and gene-specific cofactors in the regulation of eukaryotic transcription. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 63: 201–218.
Roth, S.Y., Denu, J.M. and Allis, C.D. 2001. Histone acetyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70: 81–120.
Sawadogo, M. and Roeder, R.G. 1985. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell 43: 165–175.
Sauer, F., Hansen, S.K. and Tjian, R. 1995a. Multiple TAFIIs directing synergistic activation of transcription. Science 270: 1783–1788.
Sauer, F., Hansen, S.K. and Tjian, R. 1995b. DNA template and activator-coactivator requirements for transcriptional synergism by Drosophila bicoid. Science 270: 1825–1828.
Schultz, P., Fribourg, S., Poterszman, A., Mallouh, V., Moras, D. and Egly, J.M. 2000. Molecular structure of human TFIIH. Cell 102: 599–607.
Selleck, W., Howley, R., Fang, Q., Podolny, V., Fried, M.G., Buratowski, S. and Tan, S. 2001. A histone fold TAF octamer within the yeast TFIID transcriptional coactivator. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8: 695–700.
Shen, W.C. and Green, M.R. 1997. Yeast TAF(II)145 functions as a core promoter selectivity factor, not a general coactivator. Cell 90: 615–624.
Shen, X., Mizuguchi, G., Hamiche, A. and Wu, C. 2000. A chromatin remodelling complex involved in transcription and DNA processing. Nature 406: 541–544.
Shykind, B.M., Kim, J. and Sharp, P.A. 1995. Activation of the TFIID-TFIIA complex with HMG-2. Genes Dev. 9: 1354–1365.
Shykind, B.M., Kim, J., Stewart, L., Champoux, J.J. and Sharp, P.A. 1997. Topoisomerase I enhances TFIID-TFIIA complex assembly during activation of transcription. Genes Dev. 11: 397–407.
Smale, S.T. 1997. Transcription initiation from TATA-less promoters within eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1351: 73–88.
Smith, R.L. and Johnson, A.D. 2000. Turning genes off by Ssn6-Tup1: a conserved system of transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 325–330.
Solow, S., Salunek, M., Ryan, R. and Lieberman, P.M. 2001. TAF(II) 250 phosphorylates human transcription factor IIA on serine residues important for TBP binding and transcription activity. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 15886–15892.
Sterner, D.E. and Berger, S.L. 2000. Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64: 435–459.
Sterner, D.E., Grant, P.A., Roberts, S.M., Duggan, L.J., Belotserkovskaya, R., Pacella, L.A., Winston, F., Workman, J.L. and Berger, S.L. 1999. Functional organization of the yeast SAGA complex: distinct components involved in structural integrity, nucleosome acetylation, and TATA-binding protein interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 86–98.
Stockinger, E.J., Mao, Y., Regier, M.K., Triezenberg, S.J. and Thomashow, M.F. 2001. TranscriPtional adaptor and histone acetyltransferase proteins in Arabidopsis and their interactions with CBF1, a transcriptional activator involved in cold-regulated gene expression. Nucl. Acids Res. 29: 1524–1533.
Strahl, B.D. and Allis, C.D. 2000. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403: 41–45.
Sun, X., Ma, D., Sheldon, M., Yeung, K. and Reinberg, D. 1994. Reconstitution of human TFIIA activity from recombinant polypeptides: a role in TFIID-mediated transcription. Genes Dev. 8: 2336–2348.
Tan, S., Hunziker, Y., Sargent, D.F. and Richmond, T.J. 1996. Crystal structure of a yeast TFIIA/TBP/DNA complex. Nature 381: 127–1251.
Tansey, W.P. 2001. Transcriptional activation: risky business. Genes Dev. 15: 1045–1050.
Thompson, C.M. and Young, R.A. 1995. General requirement for RNA polymerase II holoenzymes in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 4587–4590.
Thompson, C.M., Koleske, A.J., Chao, D.M. and Young, R.A. 1993. A multisubunit complex associated with the RNA polymerase II CTD and TATA-binding protein in yeast. Cell 73: 1361–1375.
Tsai, F.T. and Sigler, P.B. 2000. Structural basis of preinitiation complex assembly on human pol II promoters. EMBO J. 19: 25–36.
Upadhyaya, A.B., Lee, S.H. and DeJong, J. 1999. Identification of a general transcription factor TFIIA?/? homolog selectively expressed in testis. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 18040–18048.
Utley, R.T., Ikeda, K., Grant, P.A., Cote, J., Steger, D.J., Eberharter, A., John, S. and Workman, J.L. 1998. Transcriptional activators direct histone acetyltransferase complexes to nucleosomes. Nature 394: 498–502.
Verbsky, M.L. and Richards, E.J. 2001. Chromatin remodeling in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4: 494–500.
Verrijzer, C.P. and Tjian, R. 1996. TAFs mediate transcriptional activation and promoter selectivity. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21: 338–339.
Vignali, M., Hassan, A.H., Neely, K.E. and Workman, J.L. 2000. ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 1899–1910.
Walker, S.S., Reese, J.C., Apone, L.M. and Green, M.R. 1996. Transcription activation in cells lacking TAFIIs. Nature 383: 185–188.
Wang, G., Cantin, G.T., Stevens, J.L. and Berk, A.J. 2001a. Characterization of mediator complexes from HeLa cell nuclear extract. Mol. Cello Biol. 21: 4604–4613.
Wang, H., Huang, Z.Q., Xia, L., Feng, Q., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Strahl, B.D., Briggs, S.D., Allis, C.D., Wang, J., Tempst, P. and Zhang, Y. 2001b. Methylation of histone H4 at arginine 3 facilitating transcriptional activation by nuclear hormone receptor. Science 293: 853–857.
Wang, L., Liu, L. and Berger, S.L. 1998. Critical residues for histone acetylation by r Gcn5, functioning in Ada and SAGA complexes, are also required for transcriptional function in vivo. Genes Dev. 12: 640–653
Wang, W., Gralla, J.D. and Carey, M. 1992. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID Land TFIIA. Genes Dev. 6: 1716–1727.
Wieczorek, E., Brand, M., Jacq, X., Tora, L. 1998. Function of TAF(II)-containing complex without TBP in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature 393: 187–191.
Willy, P.J., Kobayashi, R. and Kadonaga, J.T. 2000. A basal transcription factor that activates or represses transcription. Science 290: 982–985.
Workman, J.L. and Kingston R.E. 1998. Alteration of nucleosome structure as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67: 545–579.
Workman, J.L. and Roeder, R.G. 1987. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell 51: 613–622.
Workman, J.L., Abmayr, S.M., Cromlish, W.A. and Roeder, R.G. 1988. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell 55: 211–219.
Wu, S.Y., Kershnar, E. and Chiang, C.M. 1998. TAFII-independent activation mediated by human TBP in the presence of the positive cofactor PC4. EMBO J. 17: 4478–4490.
Wu, C.H., Madabusi, L., Nishioka, H., Emanuel, P., Sypes, M., Arkhipova, I. and Gilmour, D.S. 2001. Analysis of core promoter sequences located downstream from the TATA element in the hsp70 promoter from Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 1593–1602.
Xie, X., Kokubo, T., Cohen, S.L., Mirza, U.A., Hoffmann, A., Chait, B.T., Roeder, R.G., Nakatani, Y. and Burley, S.K. 1996. Structural similarity between TAFs and the heterotetrameric core of the histone octamer. Nature 380: 316–322.
Xu, W., Edmondson, D.G. and Roth, S.Y. 1998. Mammalian GCN5 and P/CAF acetyltransferases have homologous amino-terminal domains important for recognition of nucleosomal substrates. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 5659–5669.
Xu,W., Edmondson, D.G., Evrard, Y.A., Wakamiya, M., Behringer, R.R. and Roth, S,Y. 2000. Loss of Gcn512 leads to increased apoptosis and mesodermal defects during mouse development. Nat. Genet. 26: 229–232.
Yamauchi, T., Yamauchi, J., Kuwata, T., Tamura, T., Yamashita, T., Bae, N., Westphal, H., Ozato, K. and Nakatani, Y. 2000. Distinct but overlapping roles of histone acetylase PCAF and of the closely related PCAF-B/GCN5 in mouse embryogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 11303–11306.
Yang, X.J., Ogryzko, V.V., Nishikawa, J., Howard, B.H. and Nakatani, Y. 1996. A p300/CBP-associated factor that competes with the adenoviral oncoprotein E1A. Nature 382: 319–324.
Yudkovsky, N., Ranish, J.A. and Hahn, S. 2000. A transcription reinitiation intermediate that is stabilized by activator. Nature 408: 225–229.
Zawel, L., Kumar, K.P. and Reinberg, D. 1995. Recycling of the general transcription factors during RNA polymerase II transcription. Genes Dev. 9: 1479–1490.
Zhou, Q., Lieberman, P.M., Boyer, T.G. and Berk, A.J. 1992. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 6: 1964–1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, E. Multi-protein complexes in eukaryotic gene transcription. Plant Mol Biol 50, 925–947 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021258713850
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021258713850