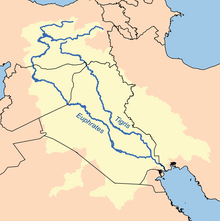
This article provides a detailed list of the cities and towns along the Euphrates River in order of country.
Cities in Turkey edit
The Euphrates is formed by the union of two branches, the Karasu or Kara River (the western Euphrates), which rises in eastern Turkey north of Erzurum, and the Murat (the eastern Euphrates). These rivers merge in the Elazığ Province of Turkey, where the river is dammed in several places such as the Keban Dam, the Karakaya Dam, Atatürk Dam, the Birecik Dam, and Karkamis Dam. Beneath the lakes of these dams are ancient towns like Samsat. Other towns like Elif, Hasanoğlu and Hisar in the Araban district of Gaziantep date back to Roman times. Halfeti, a district of Şanlıurfa, mentioned as “Halpa” in the Urartu inscriptions.[1]
The following is a partial list of other cities and towns in Turkey that border the Euphrates.
Cities in Syria edit
The upper reaches of the Euphrates flow through steep canyons and gorges, southeast across Syria, and through Iraq. From west to east, the Euphrates is in Syria joined by the Sajur, the Balikh and the Khabur. Lake Assad is a large lake in Syria on the Euphrates River formed by the construction of the Tabqa Dam in 1973. The sites of Tell Abu Hureyra and Mureybet ancient Mesopotamian cities of the Euphrates, are underneath this lake.
There are three dams along the Euphrates in Syria: First, the Baath Dam (Arabic: سد البعث, lit. 'Dam of the Renaissance') is located 22 kilometres (14 mi) upstream from the city of Raqqa in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. Second, the Tabqa Dam (Arabic: سد الطبقة), or al-Thawra Dam as it is also named (Arabic: سد الثورة, literally dam of the revolution) is located 18 kilometres (11 mi) upstream from the Baath Dam.[2] Finally, the Tishrin Dam (Arabic: سد تشرين, romanized: Sadd Tišrīn, literally October Dam) is located 90 kilometres (56 mi) east of Aleppo in Aleppo Governorate, Syria and 80 kilometres (50 mi) south of the Syro-Turkish border.
- Jarabulus—on the border of Turkey and Syria
- Maskanah is on Lake Assad
- Al-Thawrah
- Raqqa
- Abu Hamam
- Deir ez-Zor District
- Deir ez-Zor
- al-Kasrah
- Al-Busayrah is at the confluence of the Euphrates with the Khabur river.
- Al-Muhasan
- Al-Tabni
- Al-Masrab
- Khasham
- Al-Suwar
- Mayadin District
- Abu Kamal District
- Al-Salihiyah
- Al-Jalaa
- Hajin
- Al-Shaafah
- Al-Susah
- Abu Kamal (or Al-Bukamal) - on the border of Syria and Iraq
Cities in Iraq edit
In Iraq, the Euphrates is known as "Nahr al Furat". As it crosses the Syrian border, the Euphrates flows into Iraq near Al-Qa'im in Al Anbar Province. Between Anah and Haditha, the Haditha Dam creates a large lake, known as Lake Qadisiyah. Between the Syrian border and the town of Hit (in the Heet District),[3] shoals and rapids make the river commercially unnavigable. Once it reaches Hit, the Euphrates is still only navigable by very shallow-draft boats.
After Hit, Ramadi is the next major city along on the Euphrates. In Ramadi, a part of the river is diverted to feed a man-made lake called Lake Habbaniyah. The river then flows through Fallujah, and then a 550-kilometre (340 mi) canal intersects with the Euphrates 40 kilometres (25 mi) south of Baghdad to link the town of Al-Yusufiyyah (on the Euphrates) with Latifiya (on the Tigris in Baghdad) through the industrial part of Baghdad. Also, Shatt al-Hayy.
North of Basra, in southern Iraq, the river merges with the Tigris to form the Shatt al-Arab, this in turn empties into the Persian Gulf. The river used to divide into many channels at Basra, forming an extensive marshland, but the marshes were largely drained by the Saddam Hussein government in the 1990s as a means of driving out the rebellious Marsh Arabs. Since the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the drainage policy has been reversed, but it remains to be seen whether the marshes will recover.
Al Anbar Province edit
The following section lists the cities and town in order along the Euphrates river, within the Al Anbar province.
Al Qaim District edit
Anah district edit
- Al Mahdiyah
- Al Ajjamiyah
- Rawa
- Anah
Haditha District edit
Heet District edit
- Sawari
- Jaudafyah
- Samaniyah
- Jubbah (Iraq)
- Jubariyah
- Waddahiyah
- Juwaniyah
- Mashad
- Al Baghdadi
- Charraf
- Mashad (duplicate city)
- Daniqiyah
- Marabdiyah
- Yardah
- Bashiri
- Samalah
- Zara
- Kassiya
- Mashquqah
- Qabatiyah
- Sidhadiyah
- Baziyah
- Khadaram
- Mufrawda'
- Sahliyah
- Jallawiyah
- Maskhan
- Natil
- Sadqah
- Hit, Iraq
- Banrani
- Khauza
- Abu Naml
- Zuwayyah
- Aqabah
- Abu tibban
- Khan Abu Rayt
Ramadi District edit
References edit
- ^ http://newspot.byegm.gov.tr/arsiv/2001/july-aug/n15.htm[permanent dead link]
- ^ Kliot, Nurit (1994), Water Resources and Conflict in the Middle East, Milton Park: Routledge, p. 138, ISBN 0-415-09752-5
- ^ located 1,930 kilometers (1,200 mi) upstream and which is only 53 metres (58 yards) above sea level.