Palistin
Palistin Wadasatini / Padasatini | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11th century BC–9th century BC | |||||||||
| Capital | Kinalua | ||||||||
| Common languages | Luwian | ||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||
• Established | 11th century BC | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 9th century BC | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Syria Turkey | ||||||||
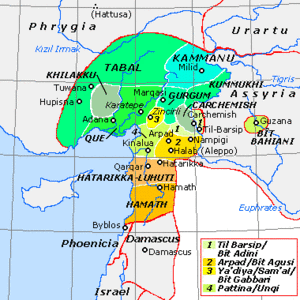
Palistin (or Walistin), was an early Syro-Hittite kingdom located in what is now northwestern Syria and the southeastern Turkish province of Hatay. Its existence was confirmed by the discovery of several inscriptions mentioning Taita, king of Palistin.

History[edit]
Palistin was one of the Syro-Hittite states that emerged in Syria after the Late Bronze Age collapse.[1]
It dates to at least the 11th century BC and is known primarily through the inscriptions of its king Taita and his wife.[1] The kingdom emerged some time soon after the collapse of the Hittite Empire, of which it is one of the successor states, and it encompassed a relatively extensive area, stretching at least from the Amouq Valley in the west, to Aleppo in the east, down to Mhardeh and Shaizar in the south.[2] Prof. Itamar Singer proposes that it was the predecessor state that, once it disintegrated, gave birth to the kingdoms of Hamath, Bit Agusi and Pattin (shortened form of Palistin).[3]
Archaeological evidence[edit]
The excavations at Tell Tayinat in the Turkish Hatay province which might have been the capital of Palistin,[4] revealed two settlements, the first being a Bronze Age Aegean farming community, and the second an Iron Age Syro-Hittite city built on top of the Aegean farming settlement.[3] Palistin is attested as Walistin in an inscription discovered in 1936 at the site.[5]
Palistin ("Watasatina") is also attested in the Sheizar Stele, which is the funerary monument of Queen Kupapiya, the wife of Taita.[6] Another stele, discovered in Meharde, might well be the funerary monument of King Taita. Both stelae mention the name of Taita, and invoke a "divine Queen of the Land", possibly the goddess Kubaba.[6] Most importantly, in 2003 a statue of King Taita bearing his inscription in Luwian was discovered during excavations conducted by German archeologist Kay Kohlmeyer in the Citadel of Aleppo.[1][7]
Possible link to Philistines[edit]
While Hittitologist John David Hawkins initially gave two transcriptions of the Aleppo inscriptions, Wadasatini and Padasatini, a later reading suggests a third possible interpretation: Palistin.[4] The similarity between Palistin and names for the Philistines,[8] such as the Ancient Egyptian Peleset and the Hebrew פְּלִשְׁתִּים Plištim, have led archaeologists Benjamin Sass[9] and Kay Kohlmeyer to hypothesize a connection. It has even been suggested, for instance, that the area around Kunulua (Calno; Tell Tayinat) may even have been part of a Philistine urheimat.[10]
Gershon Galil suggests that King David halted the Arameans’ expansion into the Land of Israel on account of his alliance with the southern Philistine kings, as well as with Toi, king of Ḥamath (mentioned in the Bible), who is identified with Taita II, king of Palistin (the northern Sea Peoples).[11]
According to Galil, there are now eight inscriptions recently discovered at different sites indicating that a large kingdom named Palistin existed in this area, which included the cities of Hamath, Aleppo and Carchemish.[12]
The proposed Palistin-Philistines link remains controversial.[2][8] According to Hittitologist Trevor Bryce, the connection between the biblical Philistines and the kingdom of Palistin remains a hypothesis and further excavations are needed to establish such a connection.[2] The Shaizar and Meharde inscriptions apparently preserve the ethnonym Walistin and there is no clear explanation for the alternation between a character signifying Wa- in the Shaizar and Meharde inscriptions and one signifying Pa- in the Aleppo inscriptions.[8]
If it was the case – as has been proposed by some theories concerning the Sea Peoples – that they originated in the Aegean area, there is no evidence from the Syro-Hittite artefacts at Tell Tayinat, either pictorial nor philological, to indicate a link to known Aegean civilizations.[3] On the contrary, most of the discoveries at Tell Tayinat indicate a typical Luwian state. To cite two examples: firstly, the Syro-Hittite inhabitants used predominantly red slipped burnished ware, which is totally different from the Aegean-type pottery used by the early farming inhabitants.[3] And secondly, the names of the kings of Palistin and the kings of the successor state of Pattin are also Hittite,[3] even though there is no evidence of a direct link between Taita and the old Hittite royal house. It has since been proposed, based on material evidence and epigraphical parallels, that some Philistines did in fact settle in Kinalua, living alongside the indigenous inhabitants before assimilating into the Luwian population of what became a typical Neo-Hittite state in all but its name, which was all that remained of the Early Iron Age Sea Peoples settlers.[3][13][14][15]
See also[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c Trevor Bryce (15 March 2012). The World of The Neo-Hittite Kingdoms: A Political and Military History. OUP Oxford. p. 128. ISBN 9780199218721. OUP Oxford, 2012
- ^ a b c Trevor Bryce (6 March 2014). Ancient Syria: A Three Thousand Year History. OUP Oxford. p. 111. ISBN 9780191002922.
- ^ a b c d e f Before and After the Storm: Crisis Years in Anatolia and Syria between the Fall of the Hittite Empire and the Beginning of a New Era (ca. 1220-1000 BC), A Symposium in Memory of Itamar Singer, University of Pavia, 2012, pp. 7–8.
- ^ a b Trevor Bryce (15 March 2012). The World of The Neo-Hittite Kingdoms: A Political and Military History. OUP Oxford. p. 129. ISBN 9780199218721.
- ^ D. T. Potts (27 April 2012). A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East. Wiley. p. 802. ISBN 9781444360769.
- ^ a b Annick Payne (17 September 2012). Iron Age Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Society of Biblical Lit. p. 47. ISBN 9781589836587.
- ^ Guy Bunnens (2006). A New Luwian Stele and the Cult of the Storm-god at Til Barsib-Masuwari. Peeters Publishers. p. 130. ISBN 9789042918177.
- ^ a b c Ann E. Killebrew (21 April 2013). The Philistines and Other "Sea Peoples" in Text and Archaeology. Society of Biblical Lit. p. 662. ISBN 9781589837218.
- ^ Benjamin Sass, Taita, King of Palistin: Ca 950-900 BCE?, University of Tel Aviv, 2010.
- ^ Julia Fridman, 2015, "Riddle of the Ages Solved: Where Did the Philistines Come From?", Haaretz (10 February 2016).
- ^ The History of King David in Light of New Epigraphic and Archeological Data Archived 2018-10-01 at the Wayback Machine haifa.ac.il 2012
- ^ The History of King David in Light of New Epigraphic and Archeological Data Archived 2018-10-01 at the Wayback Machine haifa.ac.il 2012
- ^ Emanuel, Jeffrey P. "King Taita and His Palistin: Philstine State or Neo-Hittite Kingdom?" Antiguo Oriente 13 (2015), 11–40 (link).
- ^ T. P. Harrison, "Neo-Hittites in the land of 'Palistin'. Renewed investigations at Tell Ta‘yinat on the plainof Antioch", Near Eastern Archaeology 72(4), 2009, 174–89, esp. 175.
- ^ Mark Weeden, "After the Hittites: The Kingdoms of Karkamish and Palistin in Northern Syria," Bulletin of the Institute of Classical Studies 56(2), 2015, 1–20, esp. 19.